Fire-Stones from Blackburn
The leck stone quarry in Blackburn
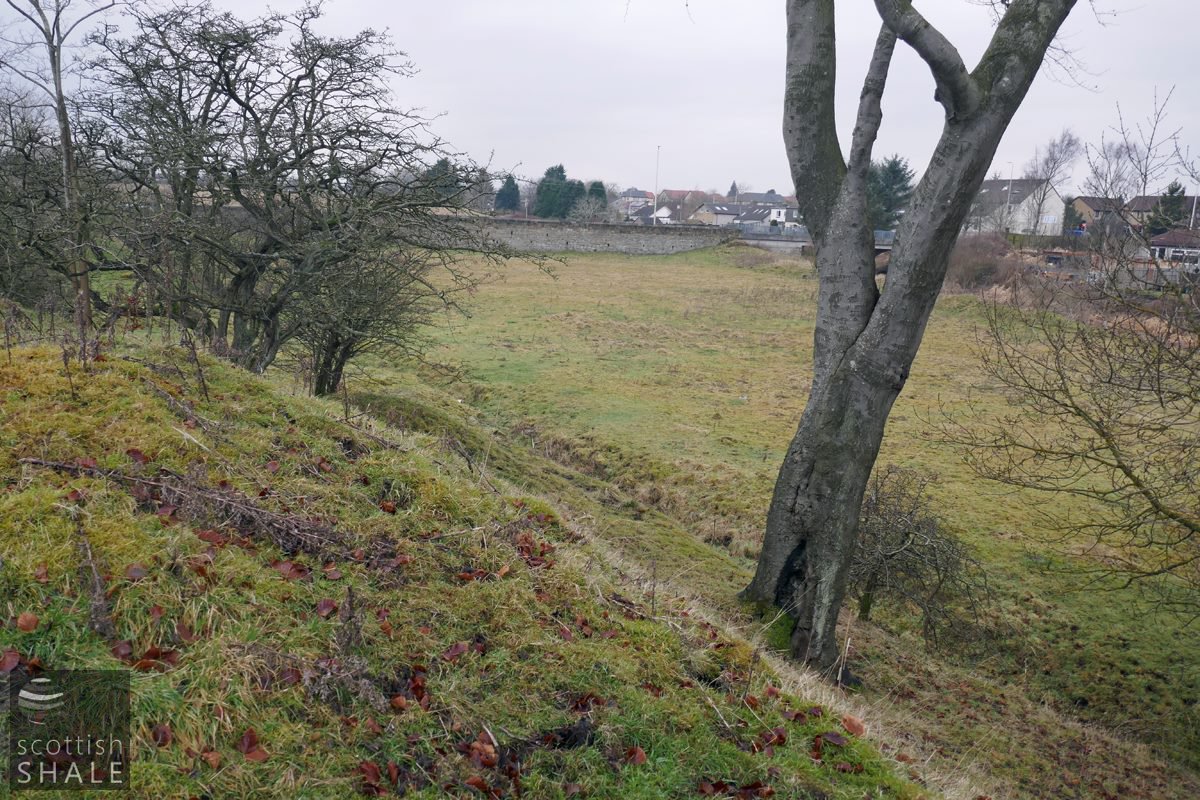

View looking from edge of quarry, across the infilled quarry area towards the bridge carrying the Blackburn to Addiewell road across the Almond.
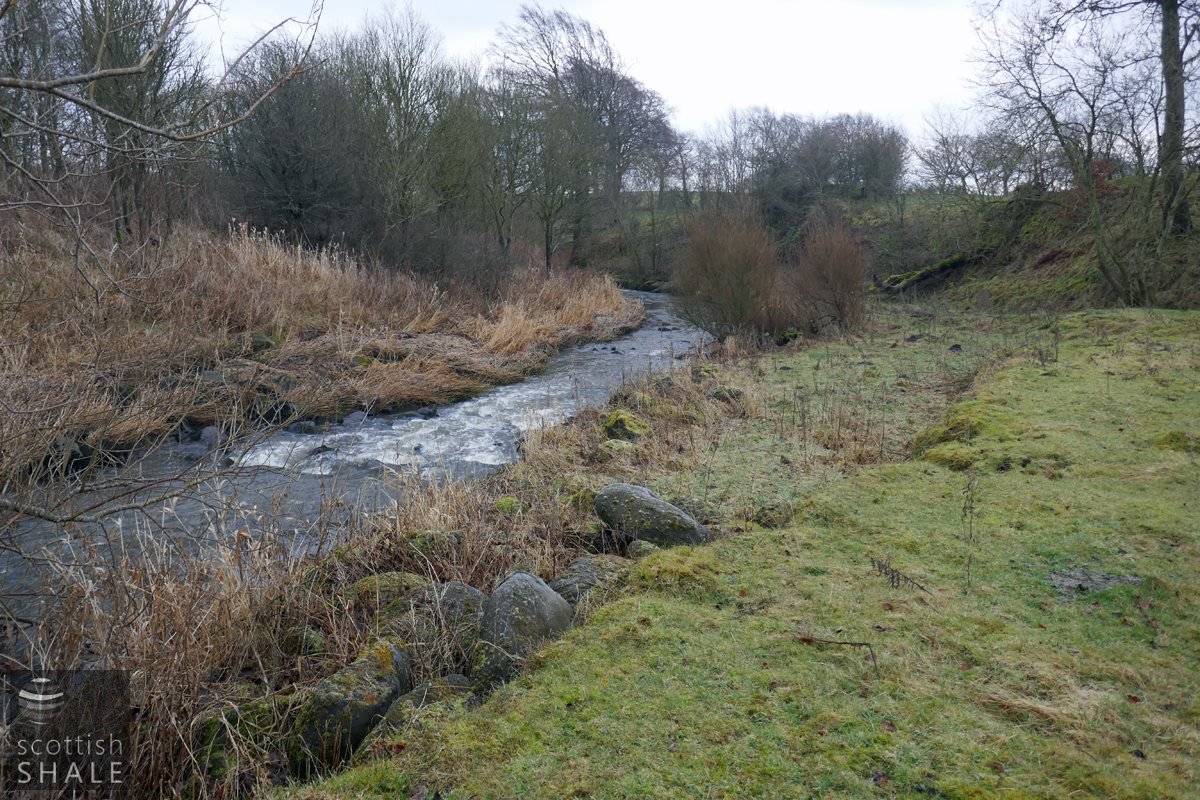

The River Almond, with site of quarry workings to the right. The stones mark the site of the former weir, directing water into the mill lade serving Hopefield Mill, removed in the early years of the 20th century.
F18002, first published 14th January 2018
For over a century, a small quarry beside the river Almond produced slabs of a special heat-resistant rock, used in many of the ovens that produced Scotland's daily bread.
The traditional “scotch” baker's oven consisted of a single arched chamber, about 3ft high, set within a substantial mass of stonework. At the close of each working day, the baker would set a coal fire within the oven chamber, leaving it to burn overnight. The next morning, the ashes would be cleared out and the day's baking done using the heat retained within the heavy stone base of the oven (the “oven sole”) and surrounding masonry. The oven sole was formed from a single slab of a special type of rock – known variously as fire-stone, oven-stone, lake-stone or leck-stone, which offered a tough, smooth surface but resisted cracking during repeated heating. This leck-stone was a form of dolerite, or similar volcanic rock, that occurred as a narrow band of hard rock intruding between layers of softer sedimentary rocks. Blackburn was one of only a handful of quarries in Scotland that produced oven soles, which might measured up to 12 ft x 9 ft and were 6 to 8 inches thick.

The oven-stone was first quarried from the haughland south of the River Almond in about 1800, and from the 1850's through to closure in 1914, the quarry was worked by the Wallace family, who had a range of other business interests in the Blackburn area. Through the years, the quarry gradually extended westwards until it reached the Blackburn to Addiewell road; also southwards into the lands of Blackburn Mains, and also to a small area of workings on the north side of the Almond. Operations were always on a modest scale, the stone having little value other than as oven soles. The working and cutting of the stone slabs seems to have been carried out manually with hammers, chisels and levers, although a steam boiler with chimney stalk powered a pump to keep the workings dry, and a steam crane is listed in the final sale of equipment in 1914.
Attending to the quarry's pumping engines late at night was not without its risks; in 1877 Peter Wallace was found dead after apparently losing his footing in the darkness and drowning, while in 1900 Richard Wallace was assaulted with a poker after a drink-fuelled brawl in the quarry engine-house at two in the morning. It seems that Blackburn was a lively and colourful place after dark.
Today, looking east from the bridge carrying the B792 over the Almond, it easy to trace the outline of the quarry, now a level in-filled area. Blackburn oven soles were sold throughout the UK and also exported to Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, therefore it seems reasonable to hope that bread ovens built around Blackburn stone will survive somewhere within historic buildings or as forgotten curiosities.
Above right: A typical Scotch bread oven, and the dictionary definition of leck-stone.
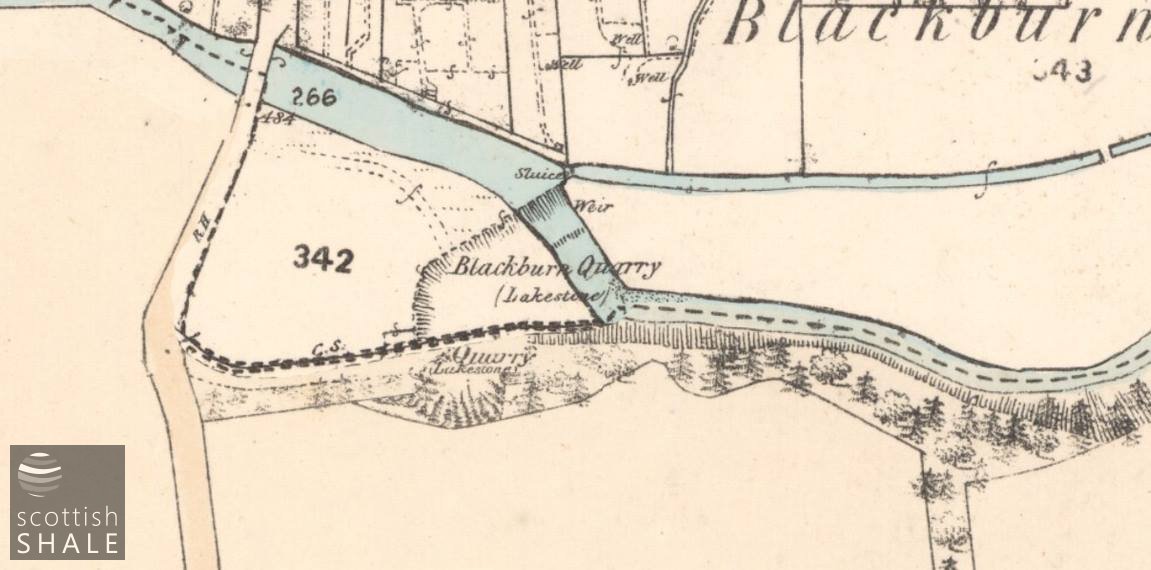
The area c.1854.
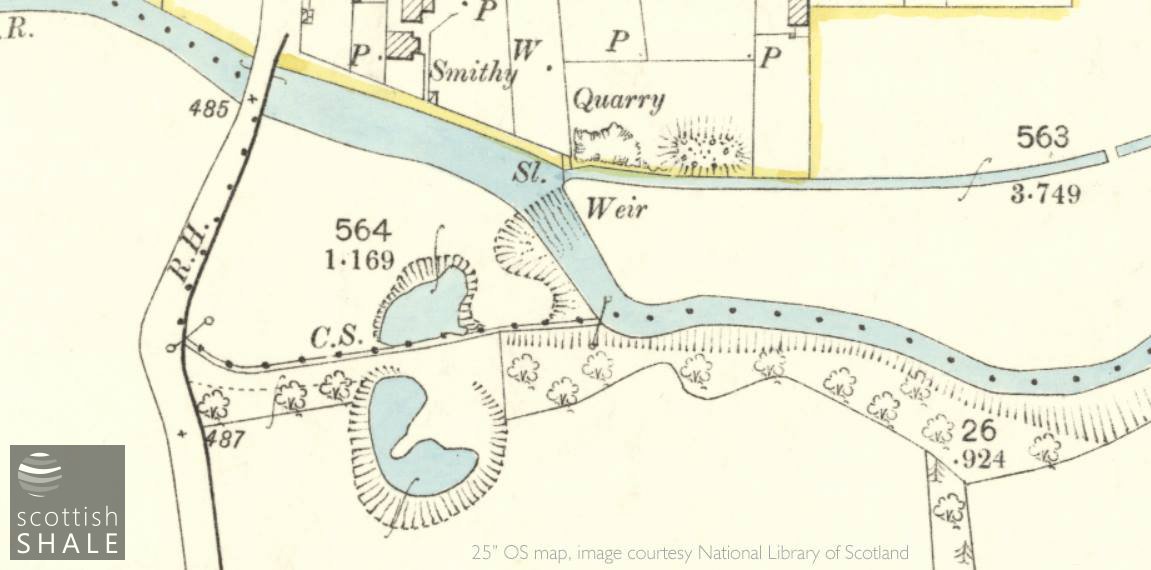
Greatly extended workings, including quarry on the north side of the river, c.1895.
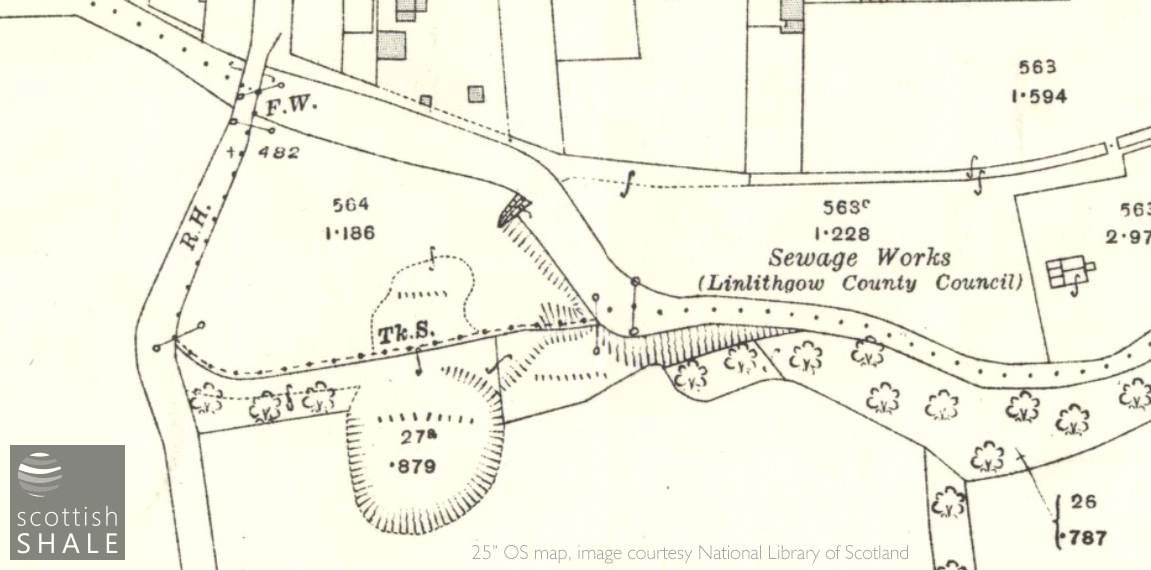
The disused quarry site c.1916.
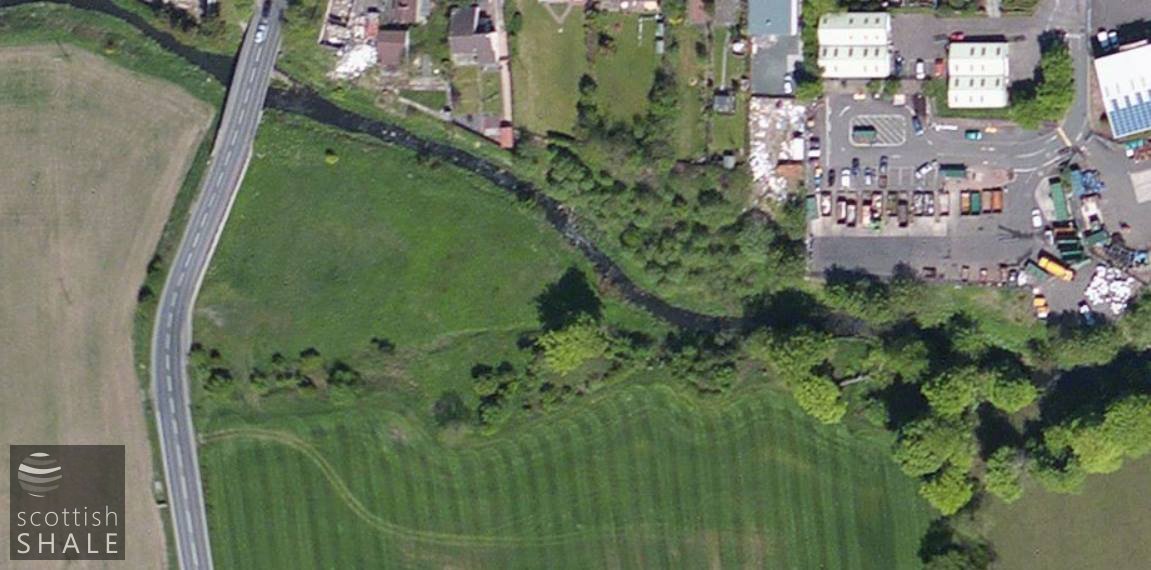

Aerial view of quarry area.
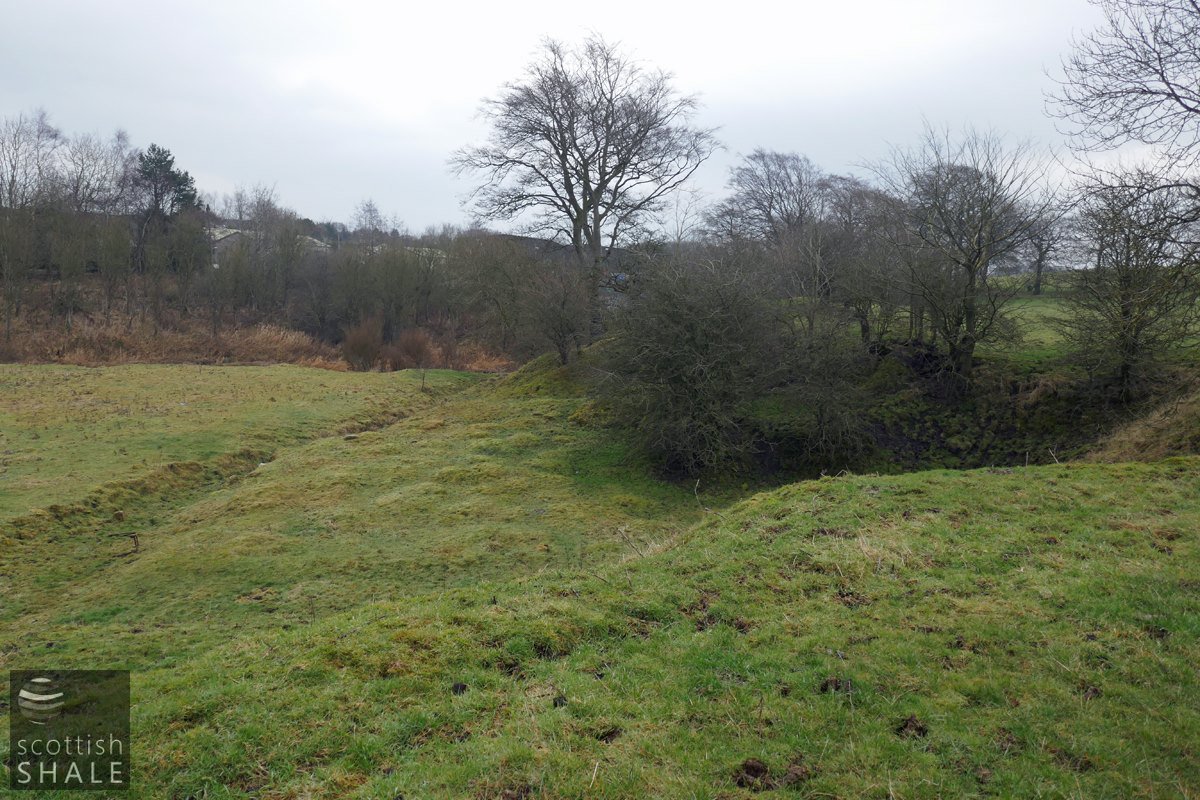

Southern extension of the quarry, crossing the parish boundary.
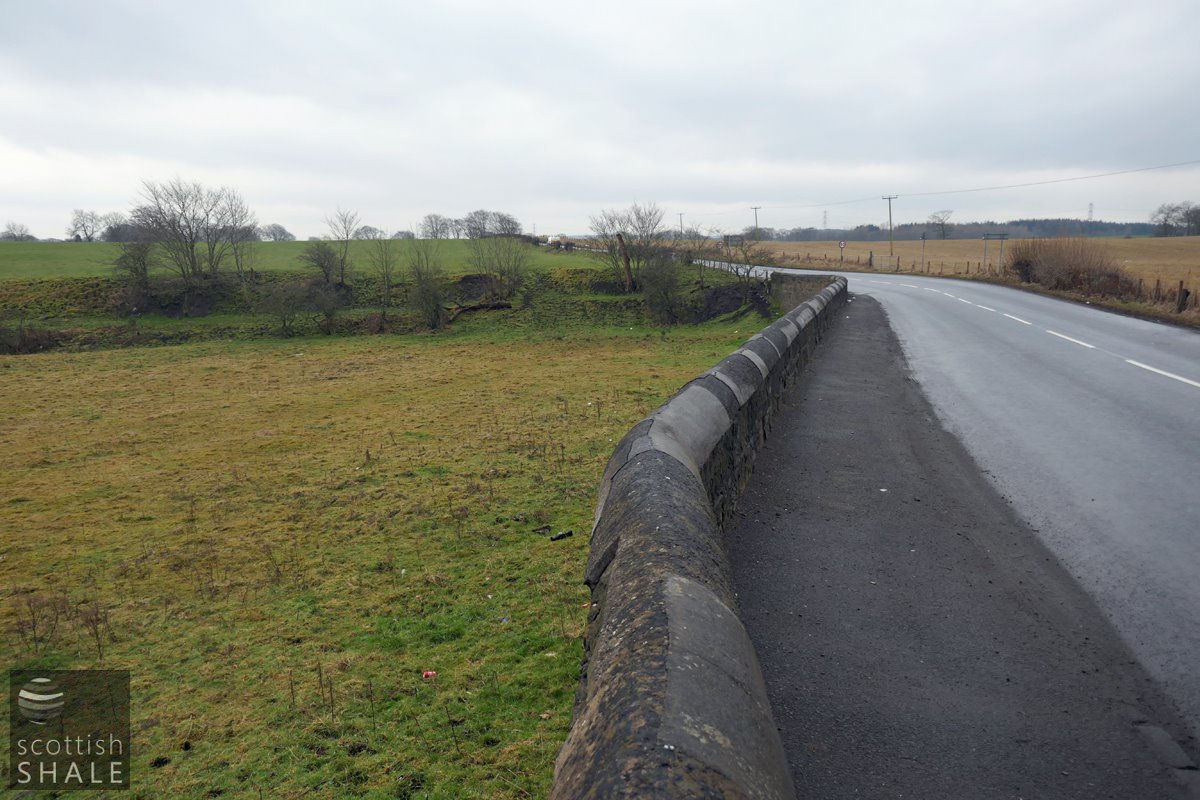

Blackburn to Addiewell road, looking south, with slope indicating the quarry edge.
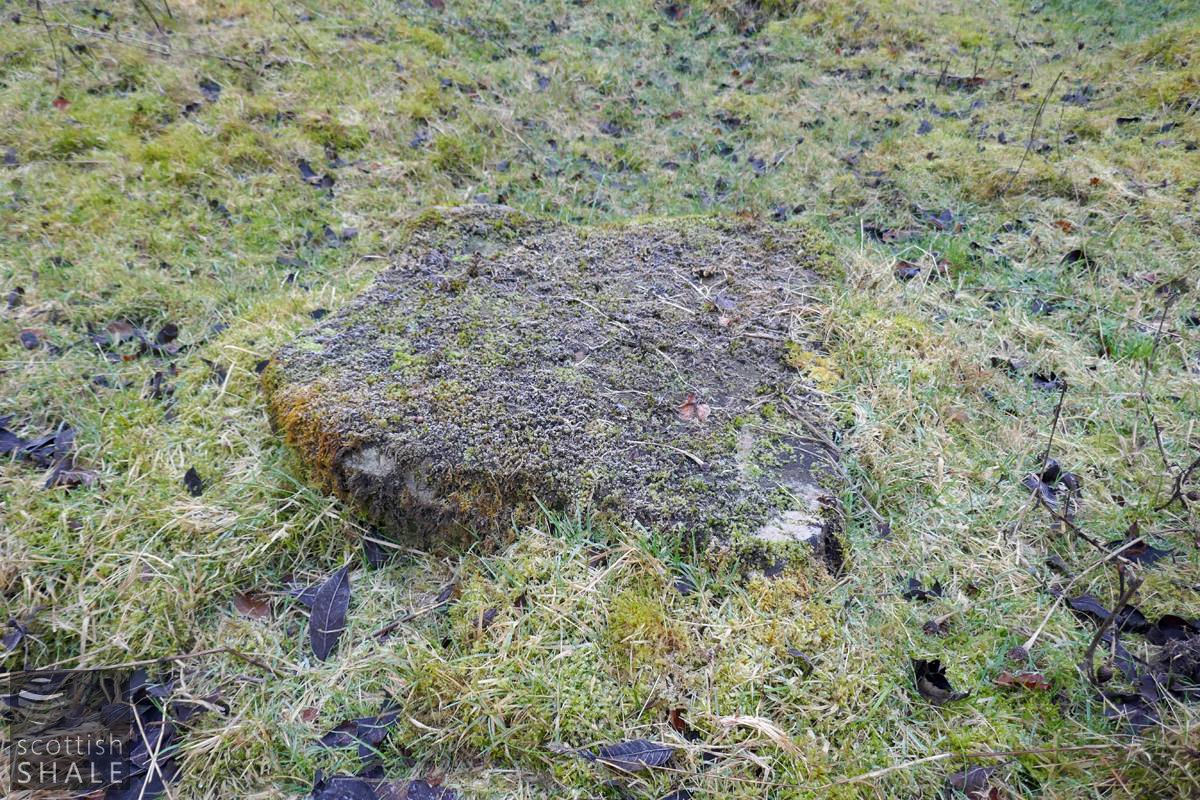

Flat, mossy stone on the quarry floor - perhaps leck-stone?
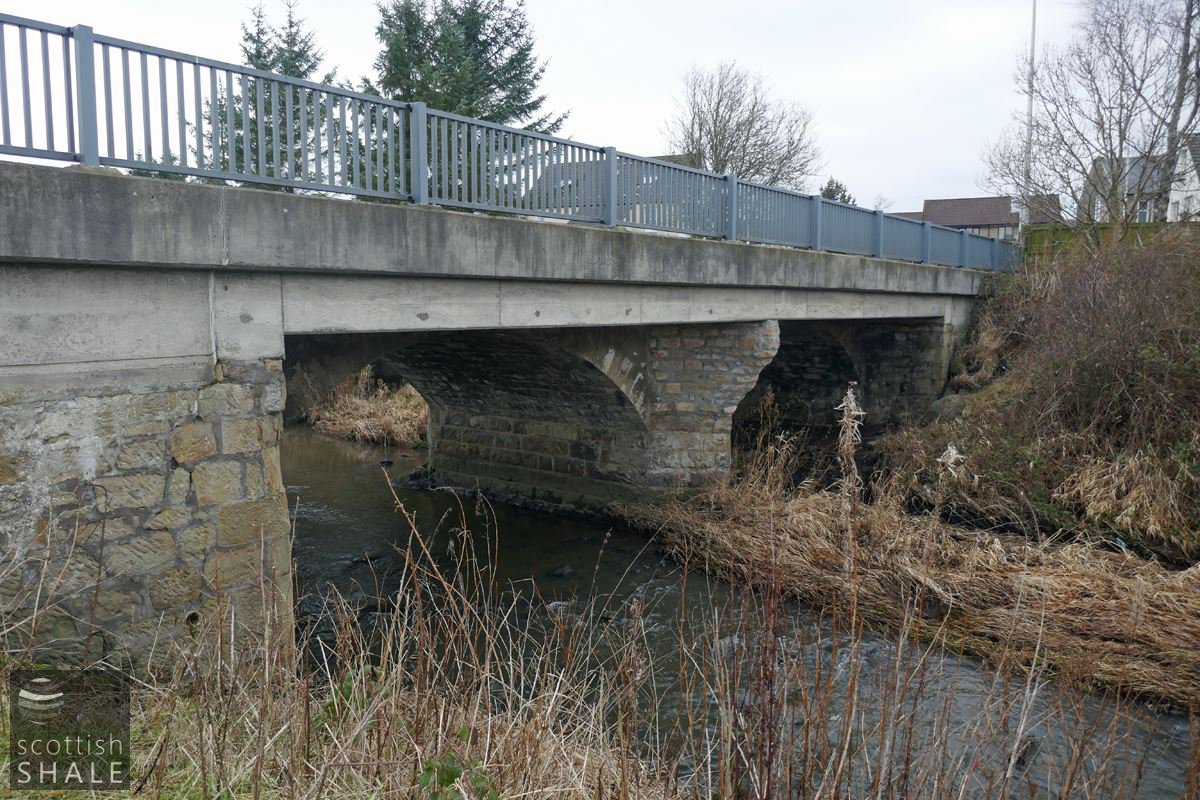

The bridge over the Almond, with concrete decking carried on the much narrower arches of the earlier bridge.
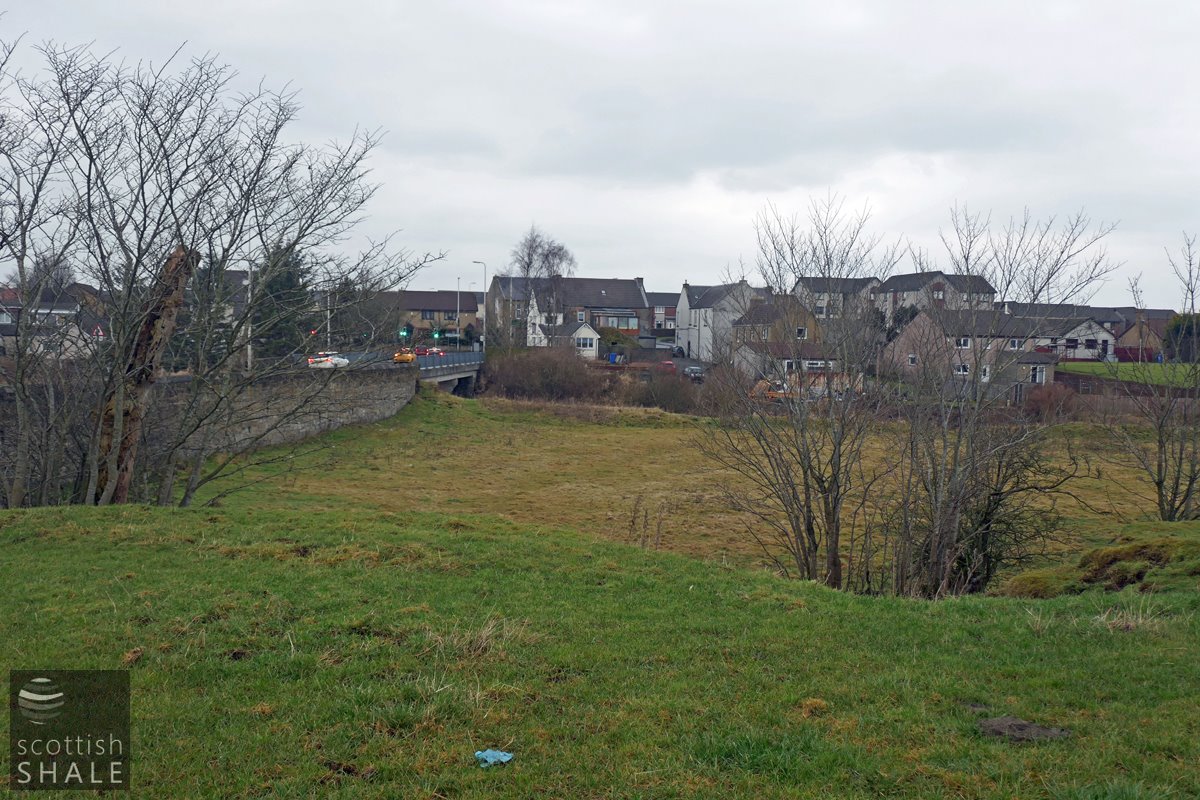

View northwards across the quarry site towards Blackburn cross.

Blackburn stone, peculiarly adapted for oven soles.

The earliest known reference to the Blackburn quarry.

Not a murder.... but some strange goings on.
The reference to Kilkenny cats is a reminder that, at that time, Blackburn had a higher proportion of those of Irish origin than any other West Lothian town.

Boys will be boys.

The final sale. The end of over a century of history.